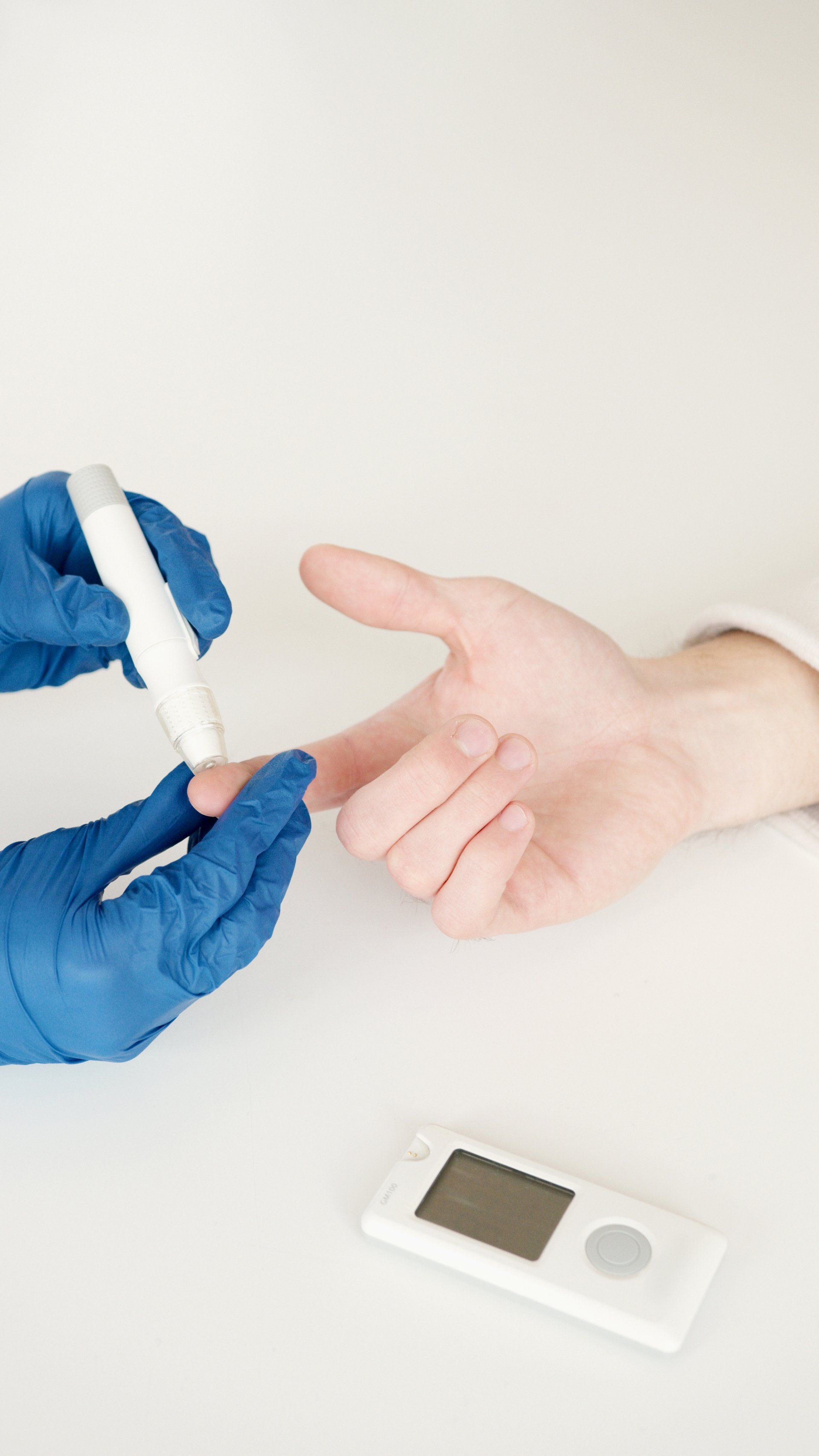
Diabetes, a chronic condition affecting millions worldwide, requires a comprehensive understanding for effective management and prevention. This article aims to demystify diabetes by defining its nature, presenting key facts, exploring its causes and symptoms, detailing its various types, and providing practical steps for prevention.
1. Defining Diabetes:
Diabetes is a chronic health condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels. This occurs when the body either does not produce enough insulin (a hormone that regulates blood sugar) or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. The result is an accumulation of glucose in the bloodstream, leading to potential complications.
2. Six (6 ) Key Facts about Diabetes:
- Prevalence: Diabetes is a global health concern, with over 400 million people affected worldwide.
- Types: There are primarily two types of diabetes—Type 1, an autoimmune condition, and Type 2, often linked to lifestyle factors.
- Insulin Resistance: In Type 2 diabetes, the body's cells become resistant to insulin, hampering glucose absorption.
- Risk Factors: Genetics, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, and poor dietary habits contribute to diabetes risk.
- Complications: Diabetes can lead to serious complications like heart disease, kidney failure, and vision impairment.
- Management: While there is no cure, diabetes can be effectively managed with lifestyle modifications, medications, and insulin therapy.
3. Causes of Diabetes:
Type 1 Diabetes: Results from the immune system attacking and destroying insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
Type 2 Diabetes: Develops when the body becomes insulin-resistant or fails to produce sufficient insulin.
4. Symptoms of Diabetes:
- Frequent urination
- Excessive thirst
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing wounds
Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management.
5. Types of Diabetes:
Type 1 Diabetes: Typically diagnosed in childhood, characterized by the inability to produce insulin.
Type 2 Diabetes: Often linked to lifestyle factors, marked by insulin resistance and impaired insulin production.
Gestational Diabetes: Occurs during pregnancy, increasing the risk of Type 2 diabetes later in life.
6. Steps to Prevent Diabetes:
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Focus on balanced meals rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engage in regular exercise to improve insulin sensitivity and maintain a healthy weight.
- Manage Stress: Practice stress-reducing techniques like meditation or yoga to regulate blood sugar levels.
- Limit Processed Foods: Reduce intake of sugary and processed foods to lower the risk of Type 2 diabetes.
- Regular Check-ups: Monitor blood sugar levels regularly and attend routine health check-ups for early detection.
Diabetes is a multifaceted condition that demands awareness, proactive measures, and effective management. By understanding its definition, key facts, causes, symptoms, and types, individuals can take informed steps towards prevention and optimal health. With a commitment to a healthy lifestyle and regular medical check-ups, the impact of diabetes can be minimized, paving the way for a healthier and more vibrant life.